For startups, every decision affects speed, scalability, and the bottom line. Choosing between CDN vs File Storage can feel like a tug-of-war between performance and cost.
The truth? Both play vital roles—but in very different ways. While one stores your data securely, the other delivers it to users worldwide faster.
Understanding how each works can save startups from paying for the wrong kind of performance. The right balance can mean smoother user experiences and lower infrastructure bills.
That’s where Filestack comes in. With powerful tools for file uploading, storage, and global delivery, it helps startups optimize both ends—storage and speed—without breaking the budget.
Let’s explore how these two technologies differ and how your startup can get the best of both worlds.
Key takeaways
- File storage keeps your data safe, organized, and scalable—acting as the long-term home for all your app’s assets.
- CDNs deliver those assets quickly through global edge servers, reducing latency and improving user experience.
- Storage scales with the amount of data you keep, while a CDN scales with the traffic and requests your app receives.
- Costs differ: storage charges per GB stored, while CDN pricing is based on data transferred.
- For security, storage focuses on redundancy and backups, while CDNs provide DDoS protection and secure global delivery.
- The best architecture for most startups is a hybrid: store files in a scalable system and deliver them fast via a CDN.
- Filestack helps you get both benefits—reliable storage and instant delivery—in a single, developer-friendly workflow.
File storage basics: your startup’s digital warehouse
Every startup needs a place to keep its digital assets safe and organized. That’s where file storage solutions come in. Think of them as your online warehouse — where every document, image, or video your app depends on is securely stored and easy to access.
In technical terms, file storage can take several forms: object storage, block storage, or cloud-based storage. Each type offers a different balance of speed, scalability, and control. Cloud storage is the most common choice for startups because it’s flexible, affordable, and quick to deploy.
Scalability is the biggest win here. As your user base grows and you begin to send large files more often, you don’t need to worry about running out of space. Storage scales automatically to match your growth. Reliability and access control are just as important—most cloud providers offer built-in redundancy and permission settings to keep data secure.
When comparing providers, startups should consider factors such as file storage cost comparisons, including the per-GB storage fee, transfer fees, and API request pricing. For example, a SaaS app that stores user-generated images or documents will benefit from a storage setup that balances price and performance without overpaying for idle capacity.
CDN fundamentals: bringing your startup’s content closer to users
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) might sound like something only big tech companies use, but it’s just as powerful—and essential—for startups. In simple terms, a CDN is a network of servers spread across the globe that stores cached versions of your content. When a user opens your website or app, the CDN delivers files from the server closest to them.
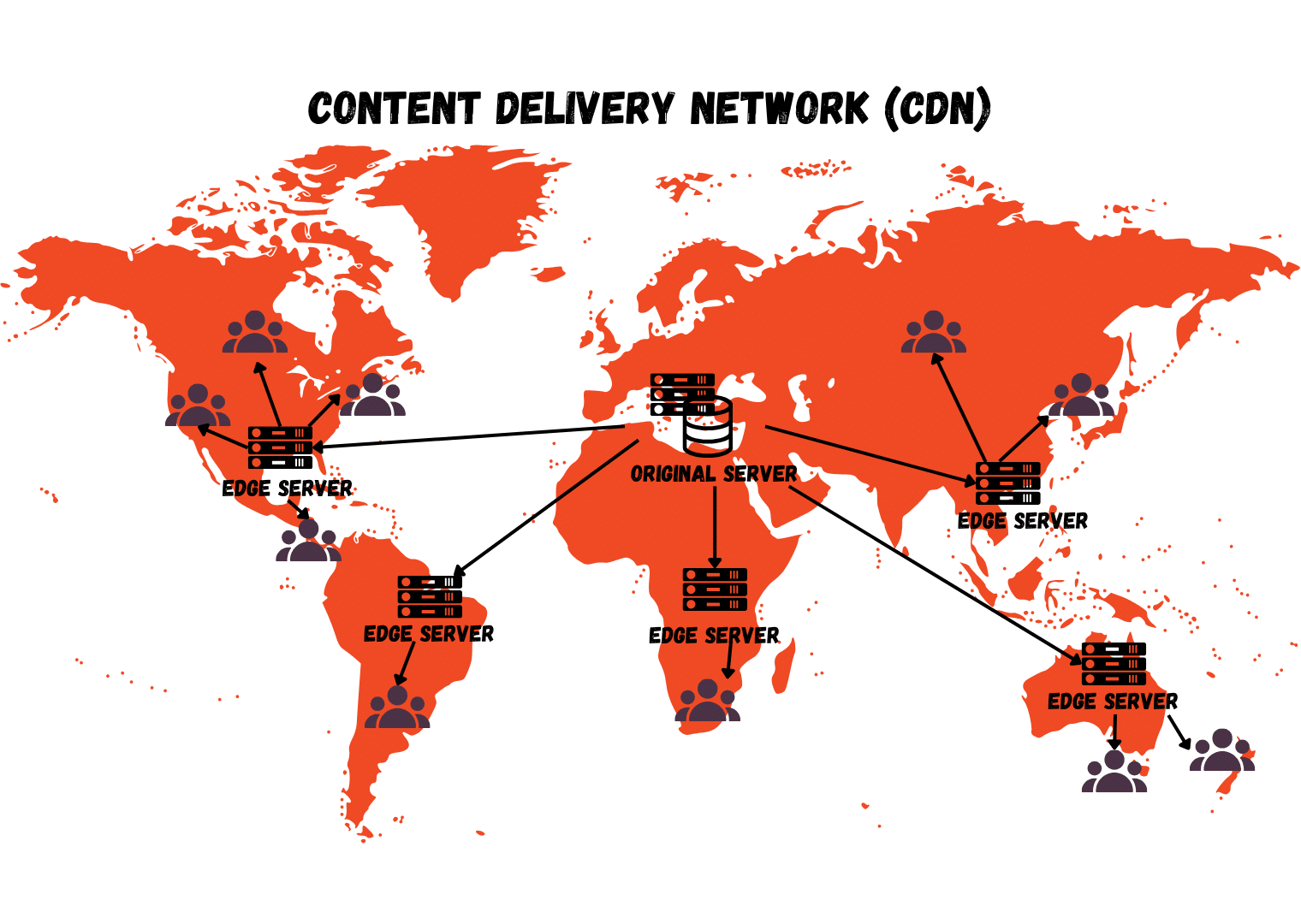
This setup cuts down on distance, reducing latency and loading times dramatically. Instead of every user connecting to a single storage location, they connect to the nearest edge server. That’s why CDN for startups is no longer a luxury—it’s a performance necessity. Fast delivery means happier users, higher engagement, and better conversions.
While CDN vs cloud storage may sound like a similar debate, the two serve different purposes. Cloud storage keeps your files safe and centralized. A CDN ensures that those same files—such as images, videos, and other static assets—reach users faster.
So, if you’ve ever wondered “what is CDN in web hosting?”, it’s the invisible engine behind smooth website experiences. Many modern hosting platforms already include CDN web hosting options because speed is now a basic expectation, not an upgrade.
6 key differences between file storage and CDN
Choosing between CDN vs File Storage isn’t about which is better—it’s about understanding what each does best. File storage keeps your data safe and accessible, while a CDN ensures that data reaches your users as quickly as possible.
For startups, the difference can mean the gap between fast, seamless user experiences and lagging, costly infrastructure. Let’s break down the six most important differences so you can decide when to rely on storage, when to lean on a CDN, and when combining both makes the most sense.
1. Purpose and functionality
At its core, file storage acts as your startup’s long-term data repository. It’s where all your assets—images, videos, backups, and documents—live securely and can be accessed or modified whenever needed. Think of it as the foundation of your app’s data layer, designed for storing, organizing, and managing information over time.
A CDN (Content Delivery Network), on the other hand, isn’t about storage—it’s about speed. It copies and caches your files across multiple servers worldwide to deliver them faster to users. While file storage focuses on keeping data safe, a CDN focuses on getting that data to your audience quickly and efficiently.
In short, file storage keeps your files at rest, while a CDN keeps them on the move. Together, they power smooth, scalable performance for modern web apps.
2. Performance and latency
When it comes to speed, CDNs win the race. A CDN reduces load time by serving content from the nearest edge server to the user. This means that whether your customer is in New York or Tokyo, they get the same fast, smooth experience.
File storage, however, isn’t designed for delivery speed. It stores your files in one or a few centralized locations, so every request has to travel back to that origin server. The farther the user is, the longer it takes for files to load.
For startups, this difference can directly affect engagement and retention. A few seconds of delay can cause users to drop off, especially in media-heavy apps. That’s why pairing CDN storage with your file system ensures your content loads instantly, no matter where your audience is.
3. Scalability and traffic handling
Scalability looks different for file storage and CDNs. In file storage, growth happens as your data increases. The more files you store—images, videos, documents—the more space you need. It’s all about capacity. Cloud-based file storage solutions make this easier by automatically expanding as your needs grow.
A CDN, however, scales based on traffic, not data size. It’s built to handle millions of requests at once by distributing them across its global network. When a sudden spike in visitors hits your app, the CDN ensures that no single server gets overloaded.
In short, storage grows with your files, while a CDN scales with your audience. For startups expecting rapid growth, using both ensures you can store unlimited data and deliver it efficiently—no slowdowns, no downtime.
4. Cost and pricing models
When it comes to costs, file storage and CDNs operate on completely different models. Storage pricing is typically based on how much data you keep — you pay per gigabyte (GB) stored each month. The more files you upload, the higher your bill. This is why startups should always review a file storage cost comparison before committing to a provider.
CDNs, however, charge mainly for data transfer — the amount of content delivered to users. This means that the more traffic your app gets, the more you’ll pay for outbound bandwidth. For most startups, CDN pricing for small businesses follows a pay-as-you-go model, which makes it easier to start small and scale gradually.
The ideal setup depends on your workload: if you’re storing massive amounts of static files, storage costs dominate; if you’re serving millions of users, delivery costs rise. Balancing both helps optimize performance and expenses as your startup grows.
5. Security and reliability
Security works differently in file storage and CDNs. File storage focuses on keeping your data safe at rest. It uses features like encryption, access control, and redundancy to make sure files are backed up and recoverable even if a server fails. This reliability is key for startups that store important documents or customer data.
A CDN, meanwhile, secures your content while it’s in motion. Most CDNs include built-in DDoS protection, SSL certificates, and firewalls to defend against attacks that could slow or crash your site. They also route traffic intelligently, so even if one node goes down, another takes over instantly.
Together, the two form a strong shield—storage protects the integrity of your data, while a CDN ensures that your users can always access it safely and smoothly.
6. Best fit for startup use cases
Knowing when to use file storage and when to use a CDN can save startups both time and money.
If your app requires storing large amounts of data—such as user profiles, uploads, or backups—file storage is the ideal solution. It’s reliable, structured, and built for managing growth over time. Startups that require consistent access to stored files without worrying about loss or corruption benefit most from this approach.
A CDN, however, shines when your priority is speed and global accessibility. If your app delivers media, images, or large downloads to users worldwide, a CDN ensures smooth performance and minimal latency.
For most startups, the most effective approach is to combine both. Use file storage for keeping data safe and organized, and a CDN to distribute it efficiently. This hybrid setup strikes a balance between cost, performance, and reliability—the perfect trio for sustainable scaling.

When startups should use both (hybrid architecture)
Most modern startups don’t choose between file storage and a CDN—they combine both. File storage handles the heavy lifting of keeping your data safe, while the CDN takes care of fast global delivery. This hybrid approach gives you the reliability of long-term storage and the performance benefits of distributed caching.
A common setup looks like this: upload files to a storage bucket, then deliver them through a CDN using an API like Filestack. It’s simple, scalable, and extremely efficient. This approach improves reliability, enhances global performance, and creates a smoother user experience—especially when your audience is spread across different regions.
Media-heavy applications benefit the most. Platforms like SaaS dashboards, e-learning tools, and creator apps often handle thousands of images, PDFs, or videos daily. By combining storage and CDN, startups get predictable infrastructure costs, low-latency delivery, and a seamless workflow from upload to display.
Code example for an e-learning tool (upload + storage + CDN delivery)
Below is a simple code example illustrating how an e-learning tool can utilize file storage for uploads and a CDN for rapid delivery. You can explore the full working demo on GitHub.
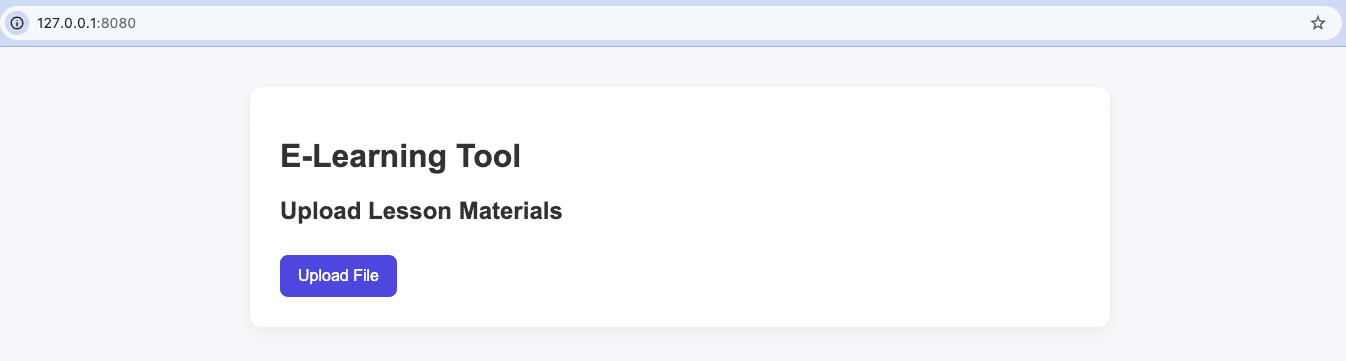
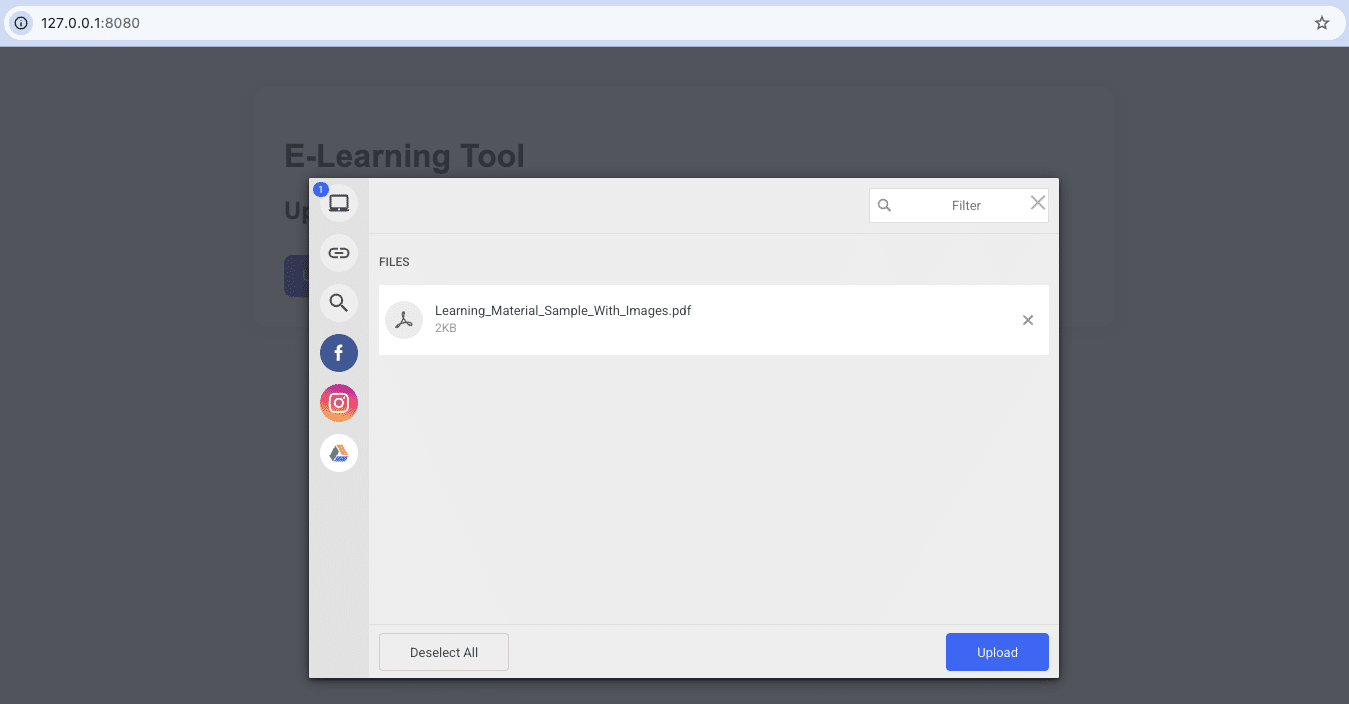
1. Frontend: Upload Learning Materials (File Picker)
For teachers to upload PDFs or video lessons:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>E-Learning Upload</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<script src="https://static.filestackapi.com/filestack-js/3.x.x/filestack.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>E-Learning Tool</h1>
<h2>Upload Lesson Materials</h2>
<button id="upload-btn">Upload File</button>
<div id="file-link"></div>
</div>
<script>
const client = filestack.init("YOUR_API_KEY"); // Replace this with your Filestack API Key
document.getElementById("upload-btn").onclick = () => {
client.picker({
accept: [".pdf", ".mp4", ".docx", "image/*"],
maxFiles: 1,
onUploadDone: (res) => {
const file = res.filesUploaded[0];
const cdnURL = `https://cdn.filestackcontent.com/${file.handle}`;
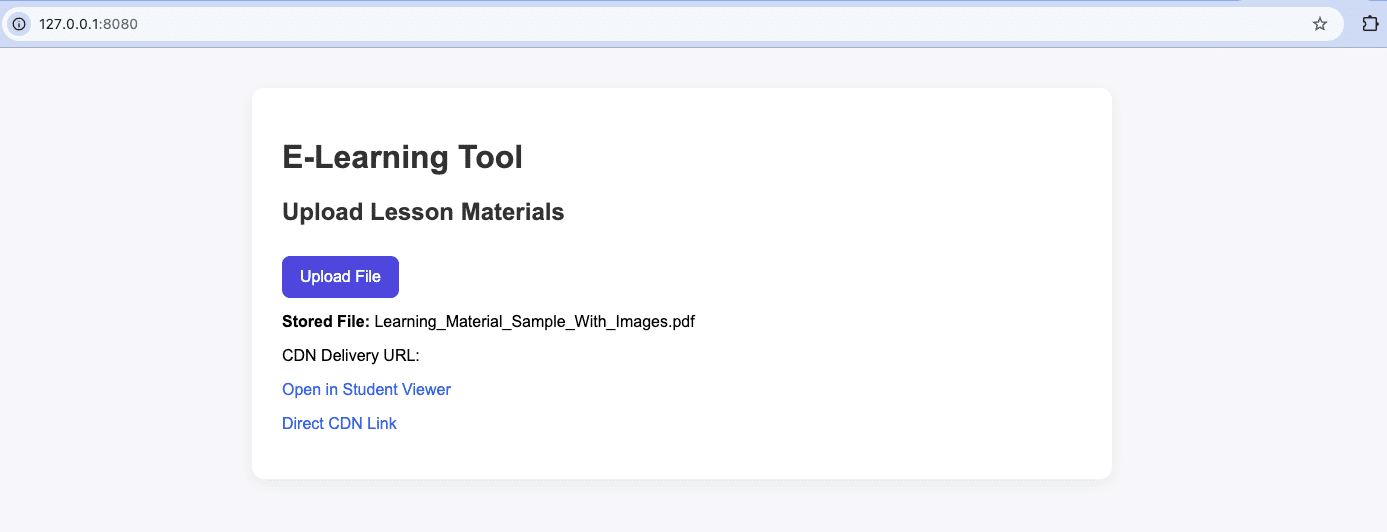
document.getElementById("file-link").innerHTML = `
<p><strong>Stored File:</strong> ${file.filename}</p>
<p>CDN Delivery URL:</p>
<p><a href="lesson-viewer.html?file=${file.handle}" target="_blank">
Open in Student Viewer
</a></p>
<p><a href="${cdnURL}" target="_blank">Direct CDN Link</a></p>
`;
}
}).open();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
What this snippet demonstrates:
- Teachers upload lesson files → Filestack file upload
- Files are stored in Filestack’s storage
- A CDN URL is automatically generated → instant delivery
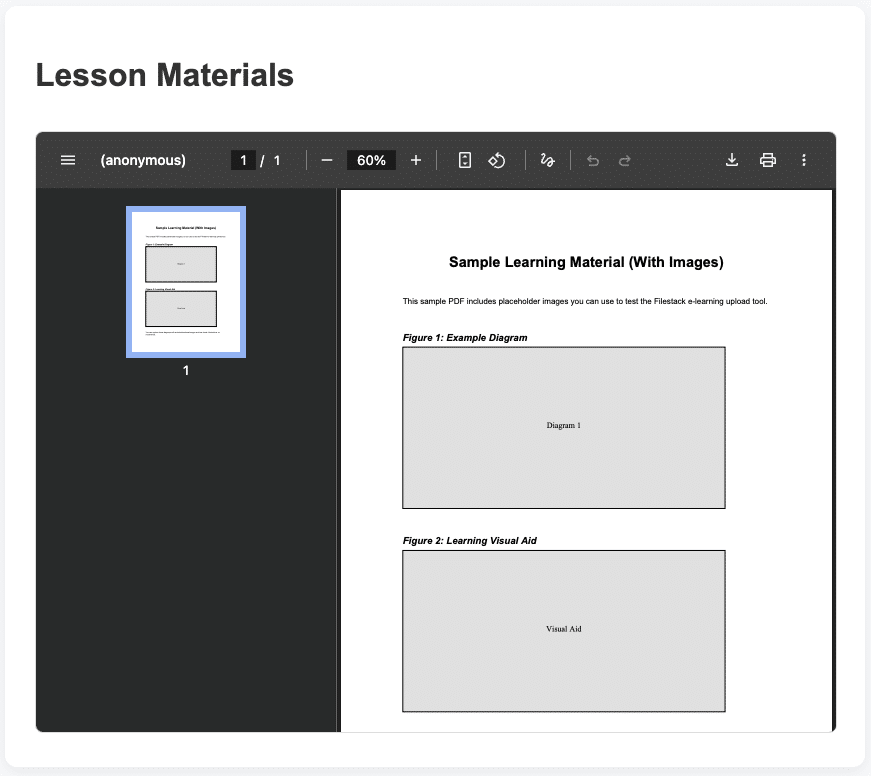
2. Displaying a lesson file using CDN delivery
For students accessing lessons instantly worldwide:
<h2>Lesson Materials</h2>
<!-- Example CDN URL returned after upload -->
<iframe
src="https://cdn.filestackcontent.com/FILE_HANDLE"
width="100%"
height="500">
</iframe>
Shows:
- Students stream videos or view PDFs directly through CDN
- Fast load times anywhere in the world
- No server strain on your app
Get your free Filestack API key and start building in minutes.
Output
Let’s run the example and see it in action.

Explore more in Filestack documentation.
Cost optimization tips for startups
Startups don’t just need fast delivery—they need cost control. The right mix of storage and CDN can help you cut costs without sacrificing performance. Start by reviewing how much data you store and how often it’s accessed. This helps you spot unnecessary storage growth and identify files that should be cached or served differently.
Using pay-as-you-go providers is another smart move. You only pay for what you actually use, which is ideal for early-stage teams. Combine this with smart caching rules to minimize outbound bandwidth and maximize the benefits of your CDN’s edge network. Performance monitoring tools also help you track bandwidth spikes, unused files, or large assets that need compression.
Conclusion
Choosing between CDN vs File Storage isn’t about picking a winner—it’s about knowing the strengths of each. File storage solutions help you keep data safe, organized, and scalable. CDNs ensure that the same data reaches users quickly, no matter where they are. Together, they solve two sides of the same challenge: cost-efficient scalability and high-performance delivery.
For most startups, the smartest path is a hybrid approach. Store your files securely, then accelerate delivery through a CDN to create the smoothest user experience. This balance keeps infrastructure costs predictable while supporting global growth.
Filestack brings both sides together with an end-to-end workflow—fast file uploading, reliable storage, and powerful CDN delivery—all optimized for startups.
Explore Filestack solutions today and build a faster, smarter, scalable product from day one.
FAQs
What is CDN in web hosting?
A CDN is a global network of servers that caches your website’s files and delivers them from the closest location to each user, making your site load faster.
Is a CDN better than file storage for startups?
No—each serves a different purpose. File storage keeps data safe, while a CDN delivers it quickly. Most startups need both.
What is the difference between CDN and cloud storage?
Cloud storage is where your files are stored. A CDN caches and delivers those files faster to users. Storage = home, CDN = delivery.
How can startups reduce file delivery costs?
Use caching, compress large files, remove unused assets, choose pay-as-you-go plans, and combine storage with CDN delivery for efficiency.
Shamal is a seasoned Software Consultant, Digital Marketing & SEO Strategist, and educator with extensive hands-on experience in the latest web technologies and development. He is also an accomplished blog orchestrator, author, and editor. Shamal holds an MBA from London Metropolitan University, a Graduate Diploma in IT from the British Computer Society, and a professional certification from the Australian Computer Society.
Read More →