Image uploads are a core feature of many of today’s web and mobile apps. For example, uploading product images on e-commerce sites or photos on social media platforms requires an image upload solution. Similarly, many other Android apps, from travel and education to food delivery and fitness apps, need an image uploader to enable users to upload images. However, creating an image upload feature isn’t as easy for developers as it seems. That’s because users today want fast and efficient apps and exceptional user experience. Therefore, developers must create quick image upload solutions that enable users to upload images quickly and seamlessly.
For instance, using a CDN to deliver images can help developers with fast image uploads. Similarly, implementing techniques for handling large image file uploads can boost the image upload speed. This article will explore various techniques for quick image upload to boost your Android app performance.
Key Takeaways
- Compressing and resizing images before uploading is crucial for speed.
- Chunking large files into smaller pieces prevents upload failures and enables resumable uploads.
- Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) significantly reduces image delivery time to users.
- Adapting upload strategies based on the user’s network condition (Wi-Fi vs. cellular) improves reliability.
- Third-party solutions like Filestack can handle these complexities, offering features like cloud integration and progress indicators out of the box.
Understanding image upload challenges in Android apps

While image upload is a simple process for users, creating image upload functionality isn’t as easy for developers. Here are common challenges developers face when implementing image upload functionality in their Android apps:
Slow uploads
Users today want fast and efficient UI. Thus, developers must focus on creating quick image upload solutions. However, various factors can affect the image upload speed, negatively impacting the user experience. For example, slow internet connections significantly affect image upload speed. It may even lead to failed uploads, leading to users’ frustration.
While slow network connection isn’t directly the app’s performance issue, it may cause the users to abandon the upload process or leave the app. However, developers can implement various techniques to mitigate this issue and enhance the user experience. For example, you can compress file size, implement resumable uploads, etc. We’ll discuss these techniques in detail later in the article.
Handling large files
Today’s modern smartphones enable users to capture high-resolution images, leading to large image file sizes. When users upload such image files on your Android app, it can significantly impact the image upload speed. That’s because large files consume lots of bandwidth and storage space. Large image files can also overload server resources, leading to slow loading times.
Fortunately, techniques like file compression, chunk and parallel uploads can help with the efficient handling of large files.
Security
With the ever-increasing cyberattacks, the security of image file uploads is a serious concern. Image files may contain sensitive information, such as location data and personally identifiable information (PII). Cybercriminals today exhaust all techniques to gain access to sensitive data and misuse it. Moreover, attackers may attempt to upload malicious image files such as executable files or scripts. These files can compromise the server or other users’ devices.
Therefore, developers must ensure secure file uploads by implementing techniques like file type validation, anti-virus scanning, etc.
Delivering an exceptional user experience
While quick image upload enhances the user experience, users today also want additional features. These include:
- Progress bars
- Image preview
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Multiple image uploads, and more.
Creating all these features from scratch can be time-consuming and challenging for Android developers. Fortunately, various quick third-party image upload solutions for Android apps are available today. Developers can use these solutions to integrate image upload functionality into their apps quickly. Moreover, these solutions often provide advanced image upload features like image preview and progress bars.
Battery consumption
Image uploads can consume a significant amount of mobile devices’ battery power. This is especially true when the upload process takes a long time due to a weak internet connection or other issues. Reduced battery life leads to users’ dissatisfaction with the app’s performance.
Filestack: A valuable solution for quick image upload
Filestack is a robust file management solution offering a wide range of powerful tools and APIs for:
- File upload
- Image transformations
- Online file delivery via CDN
- Image intelligence services, such as image tagging, OCR, facial detection, and more
Filestack also offers a specialized Android SDK that allows developers to integrate Filestack’s services into their Android apps seamlessly. The SDK supports Android 13, Google’s major update in 2022. This means developers can leverage Android 13’s advanced features and improvements. This leads to enhanced app performance, user experience, and security.
When you integrate Filestack File Uploader with Android SDK, you can enable users to upload files from their devices or select from 10 different cloud sources. These include Amazon Drive, GitHub, Dropbox, Facebook, Box, Gmail, Google Drive, and more. Uploading from cloud sources is done directly between clouds. This eliminates large mobile uploads.
Here is how you can install the Filestack Android SDK:
implementation 'com.filestack:filestack-android:13.0.0'Here is an example code for integrating the Filestack File Picker/Upload in your Android apps:
FilestackPicker picker = new FilestackPicker.Builder()
.config(...)
.storageOptions(...)
.config(...)
.autoUploadEnabled(...)
.sources(...)
.mimeTypes(...)
.multipleFilesSelectionEnabled(...)
.displayVersionInformation(...)
.build();
picker.launch(activity); //use an Activity instance to launch a picker Exploring quick image upload solutions and techniques
Here are some techniques to ensure quick image upload in your Android apps:
Image compression and optimization
Resizing and compressing images before the upload process begins is fundamental to reducing file size and ensuring fast, efficient uploads. A key challenge is striking the right balance between file size and image quality.
On Android, you can handle this natively without loading the full-resolution image into memory, which prevents OutOfMemoryError exceptions. By using the BitmapFactory.Options class and setting the inSampleSize property, you can load a downsampled version of the image. For instance, an inSampleSize of 4 loads a bitmap that is 1/16th the pixel count of the original.
Example of pre-scaling an image in native Android:
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
// Setting inSampleSize to a higher value reduces memory consumption
options.inSampleSize = 4;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(filePath, options);
Furthermore, using modern image formats like WebP is highly recommended, as it typically offers superior compression compared to traditional JPEG or PNG formats, resulting in smaller file sizes at similar quality levels.
While you can build this logic yourself, libraries like Picasso or Fresco can manage image resizing and caching efficiently. For a more comprehensive solution, Filestack’s Processing API can automate file type conversion (e.g., from PNG to WebP) and compression on the fly, directly through a simple API call.
Chunk and resumable uploads
Uploading the entire file in one go is risky for large, high-resolution images. A single network interruption can cause the whole upload to fail, forcing the user to start over. This is where chunking comes in. Chunking involves breaking a large file into smaller, manageable pieces and uploading them sequentially. If one chunk fails, you only need to re-upload that small piece.
This method is the foundation for resumable uploads, which allow a user to pause and resume an upload—or for the app to automatically recover from a lost connection—without losing progress. This significantly improves reliability and user experience, especially on unreliable mobile networks.
To implement this, you would need to build custom logic to slice the file, track the uploaded chunks on the client side, and have a server-side component to reassemble them. Alternatively, Android networking libraries like OkHttp can be used to construct multipart requests, though managing the resume logic still requires significant effort.
Managed services like Filestack abstract this complexity away entirely, providing chunking and resumable uploads out of the box to ensure high upload success rates.
Progressive image loading
You can display low-resolution versions of images while high-resolution versions are being uploaded. This provides users with immediate visual feedback and minimizes the impact of slow uploads. Thus enhancing the user experience. If you’re creating image upload functionality from scratch, you can use libraries like Glide for progressive image loading.
You can also implement progressive loading with Filestack. When you upload an image to Filestack, you can configure various processing options, including progressive rendering. By enabling progressive rendering in Filestack, you can ensure that images are delivered to users in a progressive manner, enhancing the perceived performance.
Cloud storage and CDN (content delivery network)
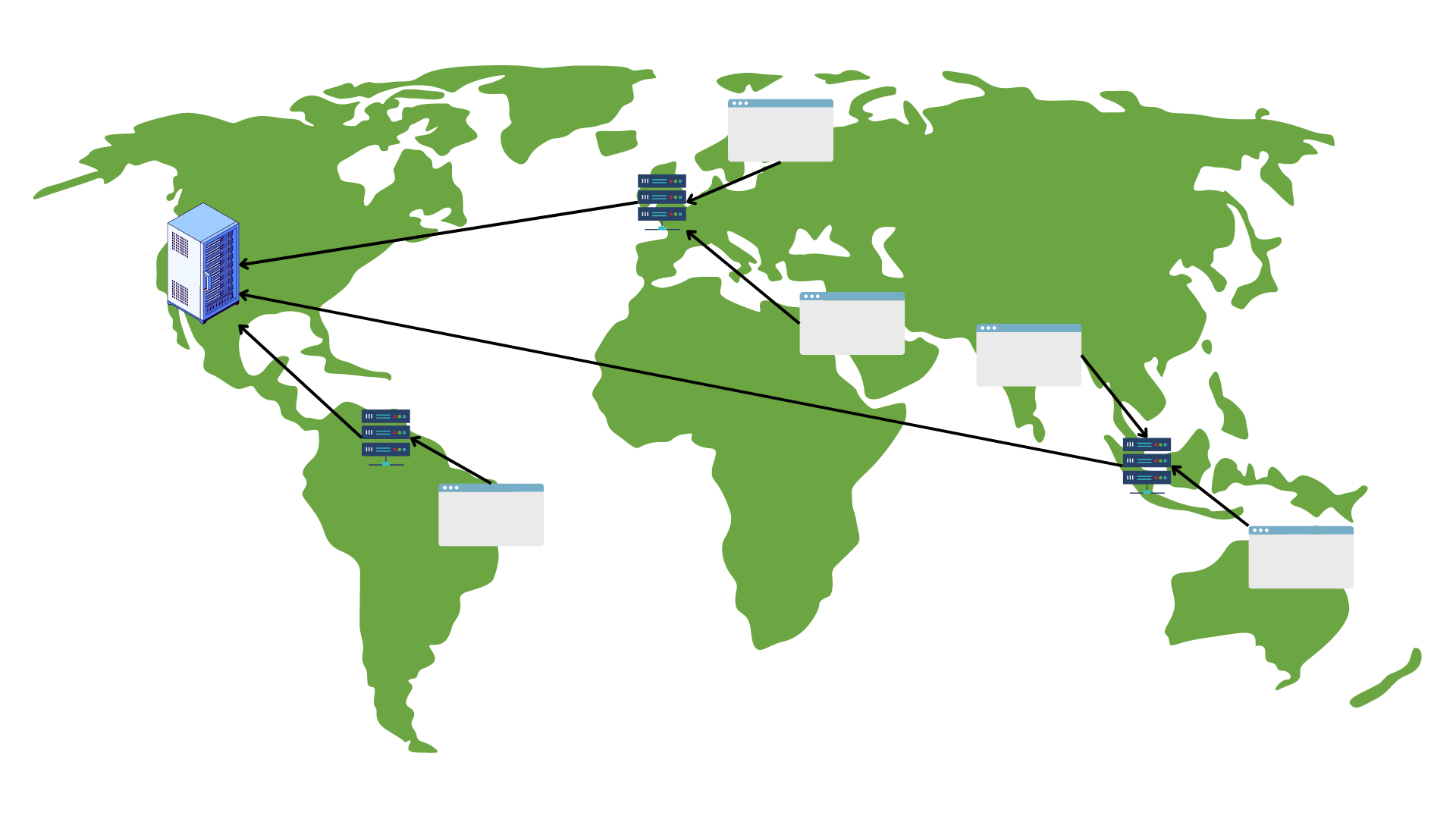
Leveraging cloud storage or a free image hosting service to store user-uploaded files can significantly boost your app’s performance. Cloud storage solutions allow you to store a large number of image files without worrying about storage space. Moreover, utilizing a CDN will enable you to deliver uploaded content/ images to users worldwide.
A CDN is essentially a network of servers and data centres distributed around the globe. It caches your app content, such as images, and stores their copies in its global servers. Then, when a user requests an asset/image, the CDN delivers it from the server nearest to the user. This reduces latency and helps deliver images online quickly.
Filestack saves all uploaded images in an S3 bucket. It also allows you to integrate your own cloud storage solution with the uploader and store images there. Moreover, with Filestack, you automatically deliver images through a powerful CDN. Once a user uploads an image through Filestack File Picker/Uploader, Filestack instantly returns a CDN URL. You can use this CDN URL to deliver images to your users quickly and seamlessly.
Adapting to Network Conditions
Not all network connections are created equal. An app that performs well on a stable Wi-Fi connection can fail miserably on a spotty cellular network. A robust application should detect the user’s network quality and adjust its upload strategy accordingly.
For instance, a developer can:
- Check Network Type: Use Android’s
ConnectivityManagerto determine if the user is on Wi-Fi or a cellular network. You might decide to only auto-upload high-resolution content when on Wi-Fi to save the user’s data plan. - Adjust Concurrency: On a fast connection, you might upload multiple images in parallel. On a slower connection, a sequential, one-by-one queue is more reliable.
- Modify Compression: You could apply more aggressive image compression when the network is poor to ensure the upload completes, even at the cost of some image quality.
Manually implementing this logic adds another layer of complexity to your app. This is a primary benefit of using a dedicated upload service. Filestack, for example, uses a feature called Intelligent Ingestion™, which automatically analyzes and adapts to changing network conditions in real-time to ensure uploads are successful and efficient.
Best practices for image uploads in Android apps
- When a file is uploading, show a progress bar or display a message like ‘uploading in just a few seconds’. Once a file is uploaded, display a message like ‘image uploaded’.
- Implement security features like file type validation, file size limitation and anti-virus scanning.
- Enable users to upload images in the background while they use other features of the app.
- Implement chunk or parallel uploads to handle large files efficiently.
- Enable users to upload multiple files simultaneously to make the upload process quicker and more efficient.
- Store uploaded content or files in cloud storage to reduce the load on the server.
- Show image file previews on the uploader.
Conclusion
Quick image upload in Android apps significantly improves the user experience and boosts the app’s performance. Some techniques and solutions for fast image uploads include:
- Image compression and optimization
- Implementing chunk and resumable uploads
- Progressive image uploading
- Storing uploaded images to the cloud
- Delivering images via a CDN
- Integration of various sources, such as Instagram and Facebook, with the uploader
- Utilizing a robust third-party quick file upload solution like Filestack.
Sign up for Filestack free and enable quick image upload in your Android apps!
Sidra is an experienced technical writer with a solid understanding of web development, APIs, AI, IoT, and related technologies. She is always eager to learn new skills and technologies.
Read More →

